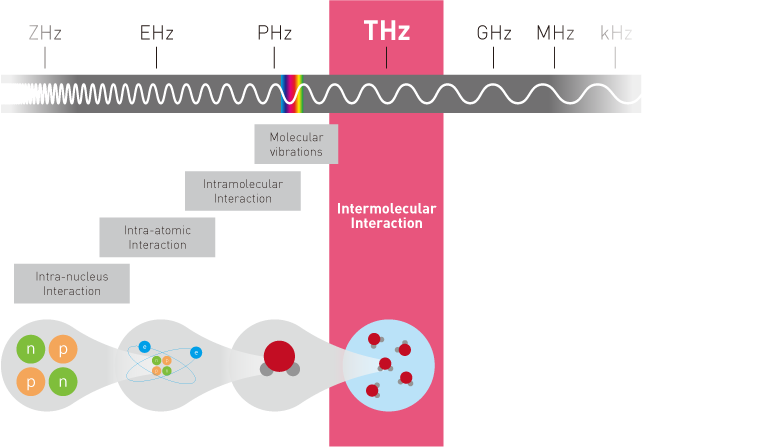
What is a terahertz wave?
An electromagnetic wave with a frequency around 1 THz (wavelength 300 µm). Although there is no clear definition of the range, it generally refers to the 300 GHz to 3 THz (wavelength 100 µm to 1 mm) band, which is the shortest wavelength after millimeter waves. It includes submillimeter waves with a wavelength of less than or equal to mm, and the long wavelength side overlaps with the millimeter wave and the broader microwave.
It hits an intermediate area between light waves and radio waves, and has the feature that an optical measurement system can be constructed. Infrared or microwave goes straight. Terahertz radiation is non-ionized submillimeter wave radiation that does not penetrate the conductor. It has the property of passing through cloth, paper, wood, plastic and ceramics. It passes through fog and clouds to some extent but does not transmit conductors such as metal and water. In the atmosphere, terahertz waves are largely attenuated by absorption by water vapor, and the propagation distance is limited.
Citation-Wikipedia
Terahertz time domain spectroscopy
In recent years, a major factor that has led to the worldwide attention of terahertz waves is the development of broadband terahertz pulse generation and detection methods using femtosecond lasers. This technique is called terahertz time domain spectroscopy and is currently the most widely used in the world [1].
A measurement sample to be measured is placed in the path through which the terahertz wave propagates, and the time waveform of the transmitted terahertz wave is detected. Using the detection signal that has detected the detection signal and the time waveform of the terahertz wave in the absence of the measurement sample, the detection signal is Fourier transformed to obtain information on the amplitude and phase of the terahertz wave.
Citation-Wikipedia